Despite the increasing popularity of wireless networks, wired serial networks are still the most reliable and robust communication method, especially in harsh environments. For industrial and building automation applications that require high levels of immunity to interference, static, and high voltage fault protection, such networks provide more efficient communication and thus uptime. This guide reviews the RS-485 protocol and discusses its reasons for widespread use in the industrial sector, as well as solutions to common problems.
RS-485 and RS-422 The RS-485 features make it the most widely used interface protocol in harsh industrial environments.
In harsh industrial and building automation networks, RS-485 transceivers are the most common physical layer interface for serial communication. The serial standard provides differential signals over two lines for long-distance, high-rate transmission for industrial applications. The RS-485 standard provides an interface to withstand harsh environments. One of the most common problems in industrial and building automation applications is the frequent switching of inductive loads, electrostatic discharges, and frequent voltage surges during operation of factory automation equipment, which can cause large electrical transients that can disrupt data transmission or cause Physical network is corrupted.

There are many commonly used data interface protocols, each of which is specific to a particular application, with specific protocol specifications and structures. Interfaces include CAN, RS-232, RS-485/RS-422, I2C, I2S, LIN, SPI, and SMBus. Among them, RS-485 and RS-422 are still one of the most reliable protocols, especially suitable for harsh industrial electrical environments such as factory and building automation.
Although RS-485 is very similar to RS-422, the two are different. The following are some of the differences between the two standards, and you need to be careful when designing your system. RS-422 is best suited for industrial environments requiring only one bus master (driver), providing data transfer mechanisms up to 10 Mbps. RS-422 uses two wires to send signals to increase the maximum baud rate and cable length. RS-422 is designed for multipoint applications where only one transmitter is connected to the bus and only one transmitter is transmitting, up to 10 receivers (Figure 1). Typical applications include process automation (chemical, brewing, paper mills), factory automation (automotive and metal manufacturing), HVAC, security, motor control and motion control.
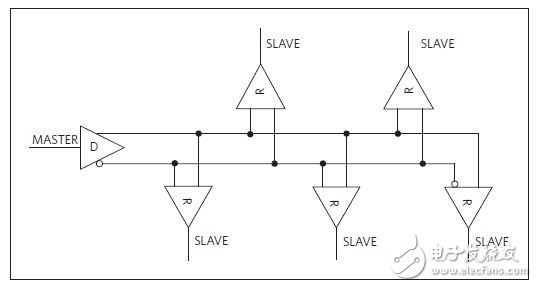
Figure 1. RS-422 multipoint bus
RS-485 offers greater flexibility when multiple bus masters/drivers are required. The standard is based on the RS-422, which increases the number of devices from 10 to 32. It has a wider common-mode and differential voltage range to ensure adequate signal voltage at maximum load. With this enhanced multipoint capability, users can build a network of devices connected to a single RS-485 serial port. Strong noise immunity and multi-point function make RS-485 the preferred serial link in industrial applications. Multiple distributed devices can be connected to PCs or other controllers through the network for data acquisition, HMI and other similar operations. . RS-485 is an extension of RS-422, so all RS-422 devices can be controlled via RS-485.
RS-485 is similar to the typical application of RS-422: process automation (chemical, brewing, paper mill), factory automation (automotive and metal manufacturing), HVAC, security, motor control and motion control. Because RS-485 increases flexibility, it is more common in both.
Learn more about RS-485As mentioned above, TIA/EIA-485, often referred to as RS-485, is the most widely used interface in the industry. RS-485 can be used for distances up to 4000 feet and speeds up to 52 Mbps, ideal for large factory environments to support the high data rates and long cable distances required for industrial automation.
The RS-485 interface can operate in half-duplex mode using a pair of transmission lines or in full-duplex mode using two pairs of lines (4-wire) to simultaneously transmit and receive data. Up to 32 drives and up to 32 receivers are supported in a half-duplex multipoint configuration. New devices with 1/4 unit load or even 1/8 unit load receiver input impedance have emerged on the market, such as the MAX13448E, which allows 128 to 256 receivers to be attached to a single bus. With this enhanced multipoint capability, users can build a large RS-485 serial device network, as shown in Figure 2.
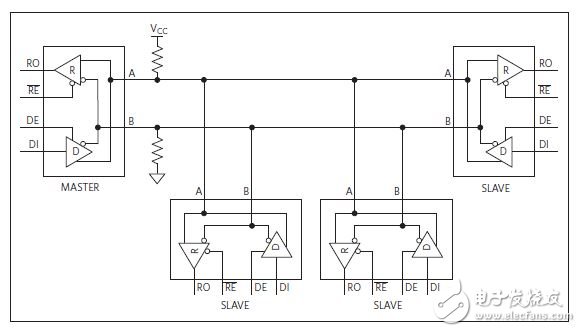
Figure 2: Multipoint Half-Duplex Transceiver System Common in Industrial Applications
The receiver input detection sensitivity is ±200mV, which means that the receiver recognizes only 1 or 0 bits when it detects a signal level higher than +200mV and below -200mV (Figure 3). Noise within the range of ±200 mV is effectively shielded. The differential signal effectively eliminates common mode noise. The minimum receiver input impedance is 12kΩ, and the driver output voltage is ±1.5V minimum and ±5V maximum.
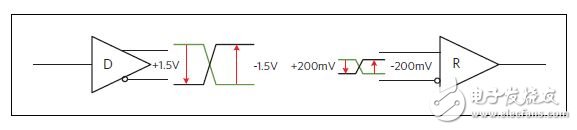
Figure 3: Minimum bus signal level for RS-485
Industrial environment challengesIndustrial system designers face many difficulties to ensure reliable operation in environmental conditions that can damage hardware or adversely affect digital communications.
pen usb stick customized,promotional pen usb flash drive,custom flash drive pens,ballpoint pen with usb flash drive,Pen with USB drive and laser pointer
Shenzhen Konchang Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.konchangs.com