As the system demands for memory capacity, bandwidth, performance, etc., the system will access multiple DRAM Devices. Different DRAM Devices have different ways of organizing, which will bring different effects. This article will give a brief introduction to the different ways of organization and its effects.
1. Single Channel DRAM Controller organization
Single Channel means that the DRAM Controller has only one set of control and data buses. In this scenario, the DRAM Controller is connected to a single or multiple DRAM Devices as follows:
1.1 Connecting a Single DRAM Device
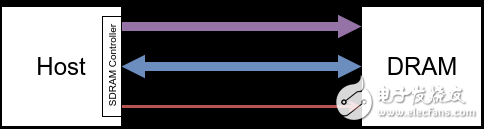
1.2 Connecting Multiple DRAM Devices
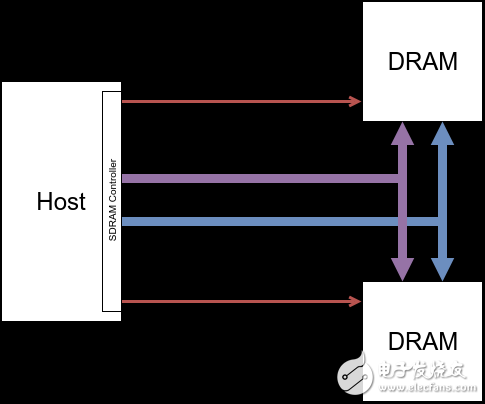
In the figure above, multiple DRAM Devices share the control and data bus, and the DRAM Controller separately accesses each DRAM Device through the Chip Select time division. In addition, when one of the devices enters the refresh cycle, the DRAM Controller can preferentially execute access requests on other devices according to a certain scheduling algorithm, thereby improving the overall memory access performance of the system.
NOTE: At the same time, only one of CS0 and CS1 can be enabled. That is, only one Device can be accessed at the same time.
This kind of organization as described above only increases the overall capacity and does not increase the bandwidth. The organization described in the figure below can increase both overall capacity and bandwidth.
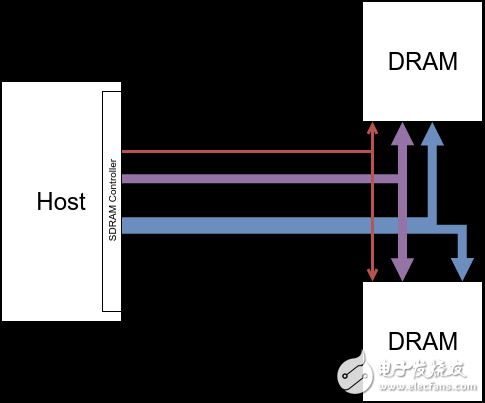
In the above figure, multiple DRAM Devices share the control bus and Chip Select signals. The DRAM Controller accesses each DRAM Devices at the same time. The data of each Device is merged together. For example, the data of Device 1 is output to the DATA[0:7] signal of the data bus. On, the data of Device 2 is output to DATA[8:15] of the data bus. In this way of organization, accessing 16 bits of data requires only one access cycle to complete without the need to break into two 8-bit access cycles.
2. MulTI Channel DRAM Controller organization
MulTI Channel means that the DRAM Controller has only multiple sets of control and data buses, and each set of buses can access DRAM Devices independently. In this scenario, the DRAM Controller is connected to DRAM Devices as follows:
2.1 Connecting Single Channel DRAM Devices
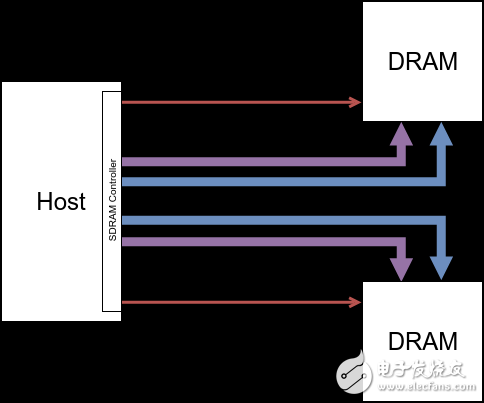
The advantage of this organization is that multiple Devices can work at the same time. The DRAM Controller can simultaneously initiate read and write requests to Devices on different Channels, which improves the throughput of read and write requests.
NOTE: CS0 and CS1 can be enabled at the same time. At the same time, two Devices can be accessed at the same time.
2.2 Connecting MulTI Channel DRAM Device
In some DRAM products, such as LPDDR3, LPDDR4, etc., the design of MulTI Channel is introduced, that is, a DRAM device includes multiple channels. In this way, the effect of simultaneous Multi Channel access can be achieved on a single Device, which ultimately leads to an increase in the throughput of read and write requests.
Comcn Electronics Limited , https://www.comencnspeaker.com