1.1 System Introduction
High-voltage circuit breakers (or high-voltage switches) can not only cut off or close the no-load current and load current in the high-voltage circuit, but also cut off the overload current and short-circuit current through the action of the relay protection device when the system fails. The perfect arc extinguishing structure and sufficient breaking capacity can be divided into: oil circuit breakers (multi-oil circuit breakers, low-oil circuit breakers), sulfur hexafluoride circuit breakers (SF6 circuit breakers), vacuum circuit breakers, compressed air circuit breakers Etc.
The high-voltage circuit breaker online monitoring system adopts advanced sensor technology, data communication technology and online monitoring technology to realize real-time on-line monitoring of the operation state and action process of the high-voltage circuit breaker; it realizes the fault diagnosis of the operating mechanism and the energy storage mechanism; Comprehensive analysis of the electrical life of the contact, and then the existence of high-voltage circuit breakers refused to move, misoperation and other hidden dangers to provide early warning for the status of high-voltage circuit breakers to provide a full basis.
High-voltage circuit breaker on-line monitoring system can be used to break the circuit breaker's breaking current and breaking times, opening coil current, closing coil current, closing and closing control power supply voltage, energy storage motor current, energy storage motor power supply voltage, circuit breaker assistance Contacts, energy storage system auxiliary contacts, contact strokes, and mechanical vibrations are monitored online and are suitable for SF6 and vacuum high-voltage circuit breakers of different 10kV and 500kV voltage levels. Multiple breakers in a substation can be real-timely processed simultaneously. Monitoring and diagnosis, monitoring data can be uploaded remotely.
The system adopts a sensor external installation method, which does not need to change the mechanical components and control system wiring of the high voltage circuit breaker in operation, has no impact on the operation of the high voltage circuit breaker, is safe and reliable, and can effectively improve the monitoring and management level of the high voltage circuit breaker.
1.2 System Structure
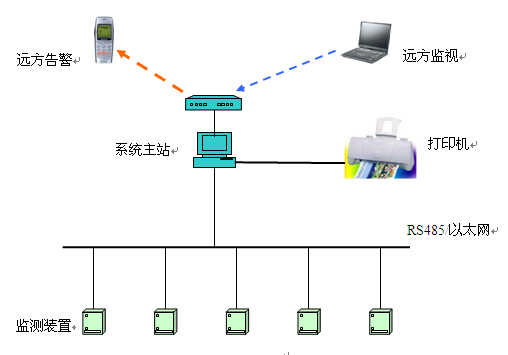
System structure
The high-voltage circuit breaker online monitoring system adopts a layered and distributed system structure. The structure is shown in the figure. The system includes three parts: the master station system, the communication system, and the distributed monitoring device.
The distributed monitoring device, also known as the lower position machine, is composed of a single-chip microcomputer system and is installed at each monitoring circuit breaker. It mainly completes the data collection of the circuit breakers' electrical parameters and mechanical parameters, and passes the communication system bus to comply with specific communication protocols. Data is uploaded to the master system. The communication system is based on the 485 bus and Ethernet and is used for the communication between the lower computer and the main station system. The main station system mainly completes the communication with the lower computer, analysis and processing of data, display of waveform curves of operation parameters, display printing of reports, comprehensive diagnosis analysis, and monitoring of lower computers.
The main station system software hierarchy is shown in the figure below. The serial communication driver is responsible for sending and receiving serial data at the hardware layer. The 101 protocol driver is responsible for link layer communication process control and data frame sending and receiving. The user data driver is responsible for the exchange of user data at each substation and interacts with the database and display operation interface. The parameter calculation driver is responsible for Calculate each parameter and interact with the database and display operator interface.
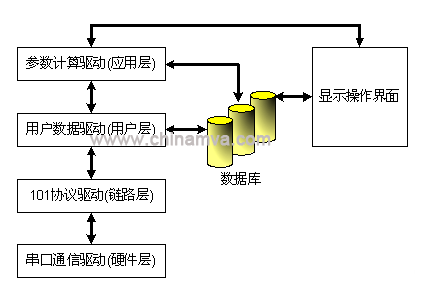
Software hierarchy
1.3 System Functions
1. Monitor and diagnose the circuit breaker operating mechanism.
1) Monitoring amount:
(1) Circuit breaker closing and opening coil current;
(2) closing control power supply voltage;
(3) Mechanical vibration during circuit breaker operation;
(4) Circuit breaker trip;
(5) Circuit breaker auxiliary contact action.
2) Diagnostic analysis and early warning and alarm
(1) Calculation of characteristic parameters of breaker operation process
(Closing time, opening time, contemporaneous, opening and closing stroke, overtravel, closing and closing speed, maximum local vibration energy, etc.);
(2) The trend analysis of characteristic parameters of circuit breaker operation process;
(3) Circuit breaker action records and statistics;
(4) Over-limit warning of characteristic parameters of breaker operation process;
(5) Circuit breaker malfunction alarm.
2. Monitor and diagnose the electrical life of circuit breaker contacts.
1) Monitoring amount:
(1) breaker breaking current, breaking times;
2) Diagnostic analysis and early warning and alarm
(1) Calculation of the electrical life of the circuit breaker (electric wear, ∫∫i2dt);
(2) Analysis of the trend of electrical life (contact wear) of circuit breakers;
(3) Circuit breaker electrical life parameter limit alarm.
3. Monitor and diagnose circuit breaker energy storage mechanisms.
1) Monitoring amount:
(1) Working current and operating time of energy storage mechanism;
(2) Energy storage motor supply voltage.
2) Diagnostic analysis and early warning and alarm
(1) Calculation of characteristic parameters of energy storage operation process (storage time, number of operations, etc.);
(2) Trend analysis of characteristic parameters of energy storage operation process;
(3) Over-limit warning of characteristic parameters of energy storage mechanism during operation;
(4) Failure of the energy storage mechanism.
1.4 Methods for Diagnosing Common Faults of High Voltage Circuit Breakers
1, operating mechanism part
1), common faults:
Switch-off and closing control of power supply failure, damage to the opening and closing coils, close-up coils, mechanical component damage, and stuck-mechanism of the mechanism cause the high-voltage circuit breaker to refuse to act, malfunction, and degraded performance.
2) Diagnostic methods:
Through the closing and closing control of the power supply voltage, it is analyzed whether there is a fault in the closing and closing control power supply.
By opening the coil current, the closing coil current, and the closing and closing control power supply voltage, it is analyzed whether the opening and closing coils and the closing coils are damaged.
By means of auxiliary contacts, contact strokes and mechanical vibrations of the circuit breakers, the timings of closing and closing, synchronization, and closing and closing speeds are analyzed to determine whether the mechanical parts are damaged or not, and whether the mechanism is stuck or not.
2, the circuit breaker contact part
1), common faults:
Contact mechanical wear, electrical wear, resulting in reduced high-voltage circuit breaker breaking performance, and even unable to break off.
2) Diagnostic methods:
Through the circuit breaker breaking current and breaking times, determine the electrical life of the circuit breaker contacts.
3, part of the energy storage mechanism
1), common faults:
Damaged energy storage motor, power failure of the energy storage motor, damage to mechanical components, and stuck mechanism, etc., causing the high-voltage energy storage motor to refuse to move and fail to store energy.
2) Diagnostic methods:
The energy storage motor power supply voltage is used to analyze whether there is a fault in the energy storage motor power supply.
Through the energy storage motor current, analyze whether there is damage to the energy storage motor coil.
Through auxiliary contacts of the energy storage mechanism, it is analyzed whether the mechanical components of the energy storage mechanism are damaged, and whether the mechanism is stuck or not.
The faults of the circuit breaker operating mechanism, energy storage system, and breaker contact parts may all cause the failure of the high voltage circuit breaker, malfunction, and degraded performance.