Not long ago, the Samsung Galaxy S8 was released, and one of its highlights was wireless charging. At the same time, Apple has successfully tested the water on the Apple Watch, using wireless charging technology, it is said that the future ihone 8 is likely to support wireless charging technology.

Generally speaking, every time people want to help a mobile phone, a computer, or other various electrical appliances, they always have to connect a charging cable. The charging cable is often too many, and it is often wrong.
With the "wireless charging" technology, as long as the phone is elegantly placed on a small, cup-like thing, it can be easily recharged without wiring. What is the secret behind such a powerful technology? And listen to Xiaobian slowly.
The role and principle of electricity and magnetismBefore exploring the principles of wireless charging technology, we must first understand the "current magnetic effect" and "electromagnetic induction."
In 1819, the Danish scientist Erst observed that if there was a current on a wire, a magnetic field would be generated around it, which would deflect the north arrow. Later generations further discovered that the wire is enclosed in a ring shape, even wound into a coil, and the generated magnetic field will be stronger and more concentrated. This is called "current magnetic effect".
In 1831, Faraday discovered that by placing a magnet or other source of magnetic field close to a coil without current, an "inductive current" would be generated on the coil, called "electromagnetic induction."
It is worth noting that the condition for electromagnetic induction is that the magnetic field should be "changed", such as the magnet getting closer or further away. If the applied magnetic field remains constant, there will be no induced current.
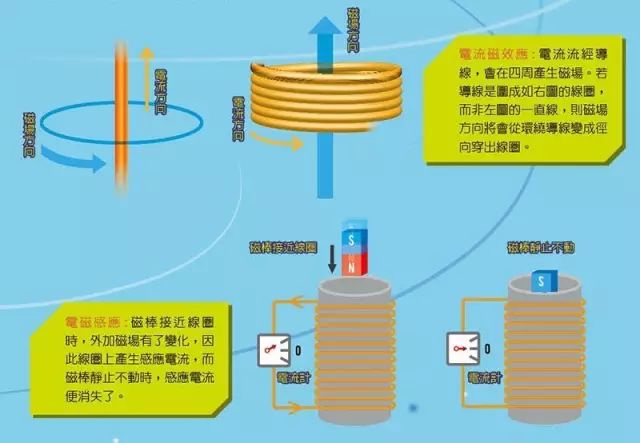
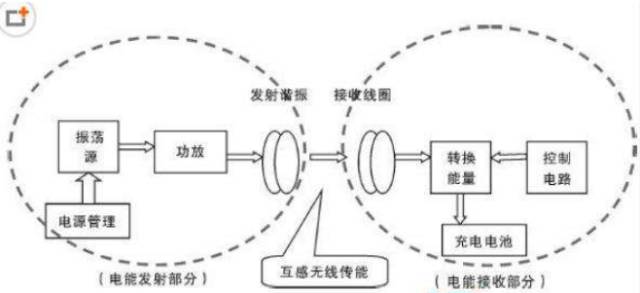
These two physical phenomena can be used simultaneously to perform wireless charging. Current wireless charging devices include a "charging stand", which is actually a coil. When the charging stand is connected to the household plug, a magnetic field is generated around the coil due to the current magnetic effect.
The electronic product to be charged also has a coil inside. When it is close to the charging stand, the magnetic field of the charging stand will generate an induced current on the coil of the electronic product through electromagnetic induction. The induction current is directed to the battery, which completes the wireless charging between the charging stand and the electronic product.
People may ask, is the magnetic field not changed to have electromagnetic induction? However, the distance between the charging stand and the charged object remains the same, so why is there electromagnetic induction?
It turns out that the electricity flowing out of the household outlet is "alternating current", that is to say, the direction of the current is constantly changing alternately, and then the flow follows, and the flow is reversed for a while. Because of this, the magnetic field generated by the charging socket coil is constantly changing direction, and does not remain unchanged, which is in accordance with the conditions of electromagnetic induction.
But unfortunately, when the smartphone or tablet is charging, as long as it is a little farther away from the charging stand, the charging efficiency will drop significantly. Even with the latest technology, the charging distance cannot exceed 5 cm.
In fact, most of the mobile devices that can be wirelessly charged are all placed on the charging stand, and there is still a difference between the wireless charging and the charging.
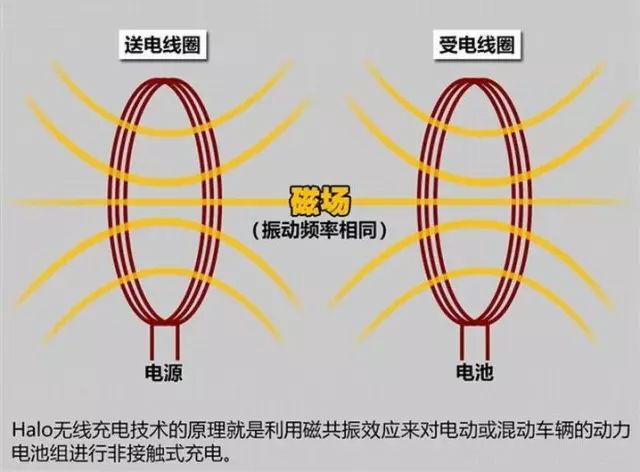
In order to increase the distance and charging efficiency of wireless charging, scientists are trying to use the principle of "magnetic resonance" for wireless charging. Add some special components such as capacitors and inductors to the circuit. When properly connected, a "resonant circuit" will be formed.
The resonant circuit can resonate, and two resonant circuits with the same vibration frequency are put together. When one of them begins to oscillate due to energization, the other circuit will also oscillate, and the current will be generated "automatically", and the electric energy will be transmitted through the space.
This phenomenon is called "magnetic resonance" and is used for wireless charging. It can make the charging distance reach several meters and the efficiency is also improved. The only difficulty is to adjust the two circuits to exactly the same frequency and for a while.
In addition to magnetic resonance, some scientists try to charge with the light energy of laser light, or even transmit it through the frequency band of the Wifi network close to the home.
Main types of wireless charging technologyAt this stage, there are four different ways of wireless charging: electromagnetic induction, electromagnetic resonance, electric field coupling, and radio wave.
Among them, the technology used for wireless charging of mobile phones is mainly electromagnetic induction technology and electromagnetic resonance technology. Of course, once wireless charging breaks through technical barriers, it will also have very broad prospects in future home appliances and electric vehicles with strong development momentum.
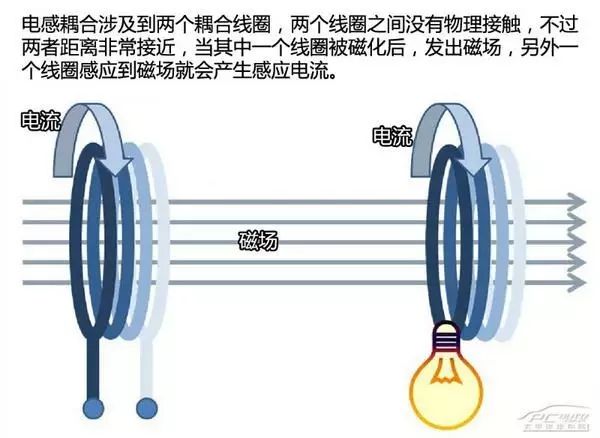
Electromagnetic induction
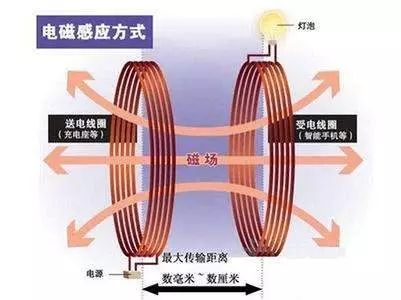
Most of the wireless charging technologies we see today use electromagnetic induction technology, and we can think of this technology as a separate transformer.
We know that the widely used transformer now consists of a core and two coils (primary coil, secondary coil); when an alternating voltage is applied across the primary coil, an alternating magnetic field is generated in the core. Thereby an alternating voltage of the same frequency is induced on the secondary coil, and the electrical energy is transmitted from the input circuit to the output circuit.
If the coil of the transmitting end and the coil of the receiving end are placed in two separate devices, when the electric energy is input to the transmitting end coil, a magnetic field is generated. When the magnetic field senses the coil at the receiving end, a current is generated, so that we construct A set of radio energy transmission systems.

The main drawback of this system is that the magnetic field rapidly decreases with increasing distance, generally only works in the range of several millimeters to 10 centimeters, plus the energy is divergent in all directions, so the induced current is much smaller than the input current. Energy efficiency is not high. But for objects that come into close contact, there is no problem.
The first wireless charging product that utilizes this principle is an electric toothbrush. The electric toothbrush is often contacted with water, so the contactless charging method is adopted, so that the charging contact point is not exposed, the waterproofness of the product is enhanced, and the whole water can be washed.
There is a coil in the charging socket and the toothbrush. When the toothbrush is placed on the charging stand, there is magnetic coupling. The principle of electromagnetic induction is used to transmit power, and the induced voltage can be rectified to charge the rechargeable battery inside the toothbrush.
The electromagnetic induction method is characterized by short transmission distance and relatively fixed use position, but high energy efficiency and simple technology, and is suitable for use as a wireless charging technology.
Electromagnetic resonance
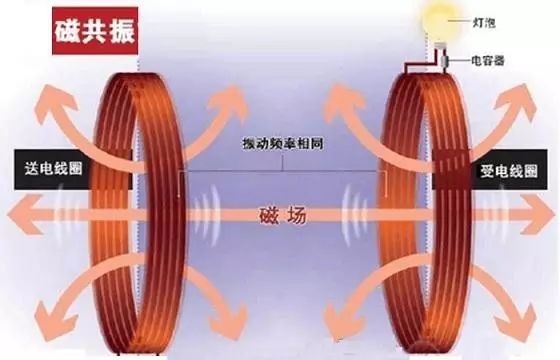
Compared with the electromagnetic induction method, the electromagnetic resonance technology has a certain tolerance in the distance, and it can support wireless charging of several centimeters to several meters, and is more flexible in use.
Electromagnetic resonance also uses two perfectly matched coils. One coil generates a magnetic field when energized, and the other coil resonates and generates current to illuminate the bulb or charge the device.
In addition to being far away, the electromagnetic resonance method can also charge multiple devices at the same time, and there is no strict restriction on the position of the device, and the flexibility of use ranks first in various technologies.
In terms of transmission efficiency, the electromagnetic resonance method can reach 40% to 60%, although it is relatively low, but it has not entered any commercialization.

The electromagnetic resonance method transmits electric energy in the form of electromagnetic wave "radio frequency" or non-radiative resonance "magnetic resonance". It has high efficiency and very good flexibility, and is the development focus of the current industry.
Electromagnetic coupling
Compared with the traditional electromagnetic induction type, the electric field coupling method has three major advantages: the position of the device has a certain degree of freedom during charging; the electrode can be made thin and easier to embed; the temperature of the electrode does not rise significantly, and it is also advantageous for embedding. .
First of all, in terms of position, although its distance can not reach the length of several meters like magnetic resonance, it is also free in the horizontal direction, and the user can charge the terminal by placing the terminal on the charging stand at will.
We can see the comparison between electric field coupling and electromagnetic induction. The misalignment between the electrodes or coils is represented by the dz/D (central point distance/diameter) parameter. When the parameter is 0, it means that the two are completely coincident. At the highest state.
When the parameter is 1, it means that the two do not coincide at all. We can see that the electric field coupling method only reduces the energy input by 20%, the device can still be charged normally, and the electromagnetic induction type is slightly wrong, the energy efficiency is rapidly decreased, and the misalignment exceeds 0.5, it is completely unable to work normally. Therefore, electromagnetic induction always requires very precise position matching.

The second characteristic of the electric field coupling method is that the electrode can be made very thin. For example, it can use copper foil or aluminum foil with a thickness of only 5 micrometers. In addition, the shape and material of the material are not required, and the transparent electrode and the thin film electrode can be used. In addition to the square shape, it can be made into any other unconventional shape.
These characteristics dictate that electric field coupling technology can be easily integrated into thin, demanding smartphone products, which is the most significant advantage of this technology over other solutions. Obviously, if the electric field coupling technology is adopted, the smartphone manufacturers have a very loose degree of freedom in designing the products, and will not suffer from the elbow in the design of the charging module.
The third advantage is that the temperature of the electrode portion does not rise - one of the problems that plagues the wireless charging technology is that the temperature at the time of charging is high, which causes the battery pack close to the electrode or the coil to be deteriorated by heat, thereby affecting the life of the battery.
The electric field coupling method does not have such a problem, and the temperature of the electrode portion does not rise, so the internal design does not have to be too deliberate. The non-heating of the electrode part is mainly due to the increase of the voltage. For example, when the voltage is raised to about 1.5 kV during charging, the current intensity flowing through the electrode is only a few milliamperes, and the heat generation of the electrode can be controlled very well.
However, the fly in the ointment is that the power supply circuit of the power transmission module and the power receiving module still generates a certain amount of heat, which generally causes the internal temperature to increase by about 10 to 20 ° C, but the circuit system can be placed at a remote location to avoid The internal battery has an effect.
The electric field coupling method has the advantages of small volume, low heat generation and high efficiency. The disadvantage is that there are few development and supporters, which is not conducive to popularization.
Microwave resonance
Intel Corporation is a proponent of microwave resonance. This technology uses microwaves as the energy transfer signal. After the receiver receives the energy wave, it is restored to the DC power available to the device through the resonant circuit and the rectifier circuit.
This method is equivalent to our commonly used Wi-Fi wireless network. Both senders and receivers each have a dedicated antenna. The difference is that this time it is not the signal but the electrical energy.
The frequency of microwaves is between 300MHz and 300GHz, and the wavelength is in the millimeter-decimeter-meter range. The ability of microwave to transmit energy is very strong. The microwave oven in our home uses its thermal effect, and Intel's microwave wireless charging technology, It is to convert the microwave energy back into an electrical signal.

The shortcomings of the microwave resonance method are quite obvious, that is, the energy is diverging in all directions, resulting in low energy utilization efficiency. For example, Intel's solution, which supplies power as low as 1 watt or less, seems to be quite limited in practical use. The advantage of this is that the position is highly flexible. As long as the device is placed near the charging device, the position requirement is very low, which is the most natural charging method.
We can see that when the two sides of the device are completely coincident, the energy efficiency of the electromagnetic induction and microwave resonance modes reach a peak, but the electromagnetic induction is obviously superior. However, as the XY direction shifts, the electromagnetic induction mode exhibits rapid attenuation, while the microwave resonance is much smoother, even if the displacement is large.
Although energy and efficiency are at a lower level, and the practical value is limited, but as a giant in the PC industry, Intel has a magical ability to decay, and its approach is also very clever: Intel designed the ultrabook as wireless The charging end of the mobile phone, the mobile phone as the receiving end, so that as long as the mobile phone is placed next to the ultrabook, it can be unknowingly and continuously charged - I believe that most users have to put the mobile phone on the desktop when they go to work. The habit, at this point the charging work can start in the background.
Even though the microwave resonance method used by Intel can only charge a very low amount of power, under the long-term charging, the power of the smart phone product will almost never be exhausted, at least from the user's point of view, because as long as he carries the notebook The computer does not need to pay attention to the charging problem at all.
Although the wireless microwave method has low energy efficiency, it is most convenient to use.
Introduction to other wireless charging technologiesUltrasonic wireless charging
A company called uBeam invented a new wireless charging mode that uses ultrasound to transport power to a distance of about 5 meters. With such a product, you can use your mobile phone to move around the house while charging while using a dedicated wireless charging kit.
uBeam's prototype is still cumbersome, but the company is working hard to reduce the size and bring it to market as soon as possible. It is reported that many companies have hoped to reach a strategic cooperation with uBeam to provide customers with such wireless space charging services to attract more passengers, including Starbucks, Virgin Atlantic, Starwood Hotels and a number of fast food chains. In addition, uBeam has also communicated with hardware vendors such as Apple and Samsung.

Many companies have tried real wireless charging, but most of them have failed, and only magnetic resonance charging has been achieved. This mode must bring the device close to the transmitter or even directly to the transmitter, so there is no major breakthrough compared to plug-in charging. However, uBeam's wireless charging model may have great potential.
Specifically, uBeam uses ultrasound-conducting technology, where the transmitter takes power through a socket or building's electrical system, then converts it into ultrasound, and then transmits the vibration to the built-in receiver—for example, with a wireless charging sleeve. After the mobile phone and receiver are responsible for converting the ultrasonic vibration into electricity, charging the mobile device. uBeam says that this mode has a charging speed similar to that of a conventional power supply.
This ultrasonic space charging method has several advantages. First of all, this technique is very safe, and it uses ultrasound similar to the ultrasound used to monitor the fetus. In addition, the price of the receiver is also very cheap, about $50, or even lower, and small size. Not only that, but these ultrasounds can also be used to transmit data and can play a role in the Internet of Things.
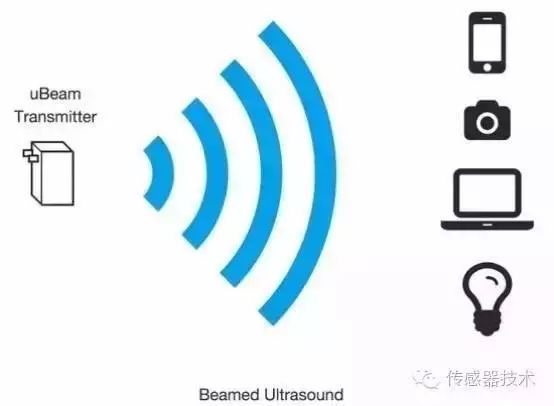
What attracts the most common users is that the technology has an effective range of about 5 meters and is equally effective for mobile devices. Although smartphones have made significant progress in terms of size and performance, battery life has not improved much, which not only undermines the user experience, but also hinders the development of the entire mobile economy. Therefore, uBeam's technology may contribute to the entire industry.
In the long run, if uBeam's wireless charging protocol really realizes its potential, it means that the wires will gradually disappear. Not only mobile phones, but also other types of electrical equipment will use this technology.
To be clear, uBeam is still overcoming some serious technical challenges, and the final product may not be able to meet expectations in terms of price, power, speed and safety. However, if you can achieve market expectations, it will become a revolutionary technology, which is the result of people's dreams.
Charging with focused light
If your smartphone runs out of power during the day, people are generally annoyed. Most people's solution is to try to remember to charge their devices at night.
Even if it is done, sometimes it is not enough for people to use it everyday. It is sometimes necessary to charge all day. For this reason, Microsoft Research has developed a potential solution: AutoCharge.
Microsoft researchers describe AutoCharge as a technology that automatically locates and charges computers on their desks. The prototype charger they built can be mounted on the ceiling and has two working modules: a monitoring module that uses Microsoft's Kinect camera to scan objects like smartphones; the other is charging mode, using UltraFire CREE XM-L T6 to focus LED light.
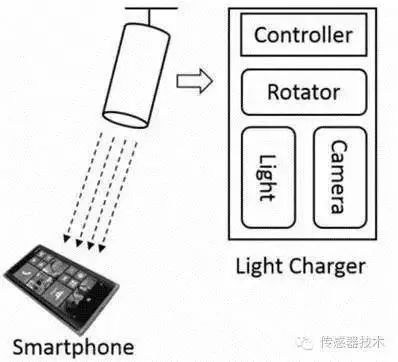
The AutoCharge system uses image-based processing to monitor and track smartphones on the table and automatically charge smartphones. The charger will continue to rotate until it detects an object that looks like a smartphone, and then uses the beam generated by solar power technology to remotely charge the smartphone. In other words, no wires are needed.
AutoCharge establishes a connection via Bluetooth or a LED on the phone and a smartphone. This ensures that charging can be stopped when the battery is fully charged, and that objects that are similar in size and shape to the smartphone cannot be charged. The system automatically shuts down within 50 milliseconds when it recognizes that an object is present between it and the smartphone, causing interference to the charge.
Wireless charging technology standardThere are currently three mainstream wireless charging standards: Power Matters Alliance (PMA) standard, Qi standard, and Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) standard.
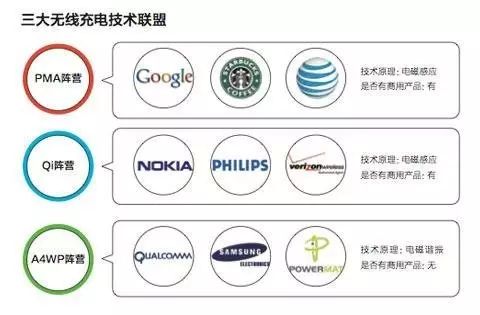
Power Matters Alliance Standard
The Power Matters Alliance standard was initiated by Duracell Powermat, which is a joint venture between P&G and wireless charging technology company Powermat, with a comprehensive strength. In addition, Powermat is a support member of the Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) standard.
At present, AT&T, Google and Starbucks have joined the PMA Alliance (short for Power Matters Alliance). The PMA Alliance is committed to creating wireless power standards for mobile and electronic devices that comply with IEEE Association standards and is a leader in wireless charging.
At present, Duracell Powermat has introduced a WiCC charging card using the Power Matters Alliance standard. The WiCC is larger than the SD card, and is internally embedded with components such as coils and electrodes for electromagnetic induction type non-contact charging. The thickness of the card is thin and can be used by inserting it into the existing smart phone battery. The terminal easily supports contactless charging.
Qi standard
Qi is the world's first wireless charging technology standardization organization - Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) launched the "wireless charging" standard, with two features of convenience and versatility.
First of all, different brands of products, as long as there is a Qi logo, you can use Qi wireless charger to charge. Secondly, it overcomes the technical bottleneck of wireless charging "universality". In the near future, mobile phones, cameras, computers and other products can be charged with Qi wireless charger, providing a possibility for large-scale application of wireless charging.

Qi uses the most mainstream electromagnetic induction technology. At present, Qi's application products in China are mainly mobile phones. This is the first stage, and will be developed into digital products of different categories or higher power in the future. So far, the number of alliance members has increased to 74, including Philips, HTC, Nokia, Samsung, Sony Ericsson, Best Buy and other well-known companies are already members of the alliance.
A4WP standard
A4WP is the abbreviation of the Alliance for Wireless Power standard, created by the wireless charging alliance created by Qualcomm, South Korea's Samsung and Powermat.

The alliance also includes members such as Ever Win Industries, Gill Industries, Peiker Acustic and SK Telecom, with the goal of setting up technical standards and industry dialogue mechanisms for wireless charging devices for electronic products, including portable electronics and electric vehicles.
The wireless charging alliance will focus on introducing "electromagnetic resonance wireless charging" technology, which is different from Qi's "electromagnetic induction technology". These two technologies have their own advantages.
The former may have lower transmission efficiency, but can achieve wireless charging at a slightly longer distance. The latter requires close contact, such as placing the phone on a base and charging it by induction without wiring, but this is more efficient.
The A4WP standard consortium hopes to make wireless charging fast and popular, allowing users to wirelessly charge anywhere. In other words, A4WP wants to make wireless charging cheaper and increase the charging interface without increasing the size of the phone, tablet or laptop, which means that more and more manufacturers will choose the wireless charger by default.
Note: The Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP) and Power Matters Alliance (PMA) two wireless charging technology alliances have now been merged. The merged alliance was renamed the AirFuel Alliance. The new name marks the two groups will work together to unify the wireless charging solution standards for smartphones and tablets as soon as possible, and compete with the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) Qi wireless charging standard.
Fork Type Terminals,Insulated Bullet Sockets Terminals,Insulated Bullet Terminals,Type Fork Insulate Terminal
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.txlyterminals.com