The method of identifying a substance based on its spectrum and determining its chemical composition and relative content is called spectral analysis. Its advantages are sensitive and rapid. Historically, many new elements have been discovered through spectral analysis, such as 铷, 铯, 氦, etc. According to the analysis principle, spectral analysis can be divided into two types: emission spectrum analysis and absorption spectrum analysis; according to the shape of the measured components, it can be divided into atomic spectrum analysis and molecular spectrum analysis. The measured component of the spectral analysis is called the atomic spectrum of the atom, and the molecular component of the measured component is called the molecular spectrum.
The emission spectrum analysis is based on the intensity of the characteristic spectrum of the atom or molecule being emitted in an excited state.
The absorption spectrum is calculated based on the characteristic spectrum of the element to be tested, by the intensity of the weakened intensity after the ground state atom of the element to be tested in the sample vapor absorbs the spectrum of the element to be measured. It complies with Langper-Beer's law:
A= -lg I/I o= -lgT = KCL
Where I is the transmitted light intensity, I0 is the emitted light intensity, T is the transmittance, and L is the light passing through the atomizer optical path since L is a constant value so A = KC.
The physical principle is:
The atoms of any element are composed of nuclei and electrons moving around the nucleus. The electrons outside the nucleus are layered according to the level of their energy to form different energy levels. Therefore, a nucleus can have multiple energy levels.
The lowest energy level is called the ground state level (E0 = 0), the other energy level is called the excited state level, and the lowest excited state is called the first excited state. Under normal conditions, the atoms are in the ground state, and the extranuclear electrons move in the orbit with the lowest energy.
If a certain external energy, such as light energy, is supplied to the ground state atom, when the external light energy E is exactly equal to the energy level difference E between the ground state and a higher energy level in the ground state atom, the atom will absorb light of this characteristic wavelength. The outer electrons transition from the ground state to the corresponding excited state. The original energy-providing light lacks some characteristic spectral lines in the spectral line after splitting, thus generating an atomic absorption spectrum.
After the electron transition to the higher energy level, it is in an excited state, but the excited state electron is unstable. After about 10-8 seconds, the excited state electron will return to the ground state or other lower energy level, and the energy absorbed by the electron transition. Released in the form of light, this process is called atomic emission spectroscopy. It can be seen that the atomic absorption spectroscopy process absorbs radiant energy, while the atomic emission spectroscopy process releases radiant energy.
spectrum analyzerAccording to the working principle of modern spectroscopy instruments, spectrometers can be divided into two categories: classic spectrometers and new spectrometers. Classical spectroscopic instruments are instruments based on the principle of spatial dispersion: new spectroscopic instruments are instruments built on the principle of modulation. Classical spectroscopy instruments are slit spectroscopy instruments. The modulation spectrometer is non-spatial spectroscopic, which uses circular aperture to enter the light according to the principle of splitting of the dispersive component. Spectroscopic instruments can be divided into: prism spectrometer, diffraction grating spectrometer and interference spectrometer.
OpTIcal MulTI-channel Analyzer is a new type of spectrum analysis instrument that has been used in photopic detectors (CCD) and computer control for more than a decade. It integrates information acquisition, processing and storage functions. Since OMA no longer uses photographic emulsions, avoiding and eliminating the darkroom processing and subsequent cumbersome processing, the measurement work has fundamentally changed the traditional spectroscopy technology, greatly improving the working conditions and improving the work efficiency: using OMA Analytical spectroscopy, accurate and rapid measurement of the basin, high sensitivity, fast response time, high spectral resolution, measurement results can be immediately read from the display or output by the printer, plotter. It has been widely used in almost all spectral measurement, analysis and research work, especially for the detection of weak signals and transient signals.
How the spectrum analyzer worksAtomic emission spectroscopy is the determination of the chemical composition of a substance based on the spectrum emitted by the atom. Different substances are composed of atoms of different elements, and the atoms contain a tightly structured nucleus surrounded by electrons that move continuously. Each electron is at a certain energy level and has a certain amount of energy. Under normal conditions, the atom is in a stable state and its energy is the lowest. This state is called the ground state. But when an atom is subjected to energy (such as heat, electricity, etc.), the atom acquires energy by colliding with high-speed moving gaseous particles and electrons, causing the electrons in the outer layer of the atom to transition from the ground state to a higher energy level. An atom in this state is called an excited state. The energy required for an electron to transition from a ground state to an excited state is called an excitation potential. When the applied energy is large enough, the electrons in the atom are separated from the nucleus and the atom becomes an ion. This process is called ionization. The energy required for an atom to lose an electron to become an ion is called the first-order ionization potential. The outer electrons in the ions can also be excited, and the energy required is the excitation potential of the corresponding ions. The atoms in the excited state are very unstable and transition to the ground state or other lower energy levels in a very short time.
When an atom transitions from a higher energy level to a ground state or other lower energy level, excess energy is released, which is radiated in the form of electromagnetic waves of a certain wavelength, and the energy of the radiation can be expressed by the following formula (1) E2 and E1 are energy of high energy level and low energy level, h is Planck constant; v and λ are respectively the frequency and wavelength of the emitted electromagnetic wave, and c is the speed of light in vacuum.
The wavelength of each line emitted depends on the difference between the two energy levels before and after the transition. Since the atom has many energy levels, the outer electrons can have different transitions after being excited, but these transitions should follow certain rules (ie, "spectral law"), so a series of atoms for a particular element can produce a series of Characteristic spectral lines of different wavelengths, which are arranged in a certain order and maintain a certain intensity ratio. Spectral analysis is to identify the presence of elements (qualitative analysis) by identifying the characteristic spectra of these elements, and the intensity of these spectral lines is related to the content of the elements in the sample, so the intensity of these lines can be used to determine the elements. Content (quantitative analysis). This is the basic basis for emission spectroscopy.
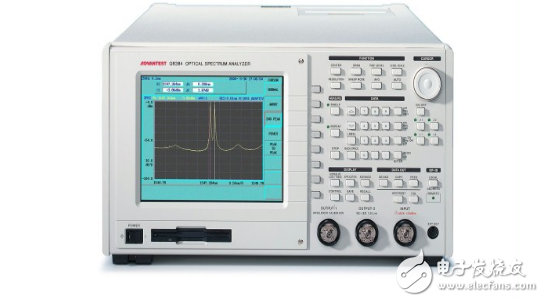
What is the use of the spectrum analyzer?Spectrometers, also known as spectrometers, are widely known as direct reading spectrometers. A device for measuring the intensity of different wavelength positions of a line by a photodetector such as a photomultiplier tube. The construction consists of an entrance slit, a dispersion system, an imaging system and one or more exit slits. The dispersive element separates the electromagnetic radiation of the radiation source into a desired wavelength or wavelength region and performs intensity measurement at a selected wavelength (or scanning a certain wavelength band). Divided into two kinds of monochromator and multicolor instrument.
constitute
A typical spectrometer consists primarily of an optical platform and a detection system. It includes the following main sections:
1. Incident slit: The object point of the spectroscopic imaging system is formed under the illumination of incident light.
2. Collimating element: Makes the light from the slit into parallel light. The collimating element can be a separate lens, mirror, or directly integrated on the dispersive element, such as a concave grating in a concave grating spectrometer.
3. Dispersive components: Gratings are usually used to spatially disperse optical signals into multiple beams.
4. Focusing element: Focusing the dispersive beam so that it forms an image of a series of incident slits on the focal plane, where each image point corresponds to a particular wavelength.
5. Detector array: placed in the focal plane to measure the light intensity of each wavelength image point. The detector array can be a CCD array or other type of photodetector array.

Spectrometers are widely used in agriculture, astronomy, automotive, biology, chemistry, coating, colorimetry, environmental testing, film industry, food, printing, paper, Raman spectroscopy, semiconductor industry, component testing, color mixing and matching, biology Medical applications, fluorescence measurement, gem composition detection, oxygen concentration sensor, vacuum chamber coating process monitoring, film thickness measurement, LED measurement, emission spectrum measurement, UV/Vis absorption spectroscopy measurement, color measurement and other fields are widely used.
Conclusion: Through the above introduction, I believe that everyone has a preliminary understanding of the specific situation of the spectrum analyzer, and at the same time the specific application of the spectrum analyzer in China's science.
Front Screen Glass Lens For Iphone
Glass Cover For Iphone,Front Screen Outer Glass Lens,Glass Cover With Oca,Glass Cover For Touch Screen
Shenzhen Xiangying touch photoelectric co., ltd. , https://www.starstp.com