The pins of the FPGA mainly include: user I/O (User I/O), configuration pins, power supply, clock, and special application pins. Some of these pins can be used for a variety of purposes, so before designing the FPGA circuit, you need to carefully read the chip manual for the corresponding FPGA.
Let's take the Cyclone series FPGA of ALTEra as an example to introduce various function pins of FPGA.
(1) User I/O.
I/Onum (LVDSnumn): Can be used as an input or output, or a bidirectional port, and can be used as the negative terminal of an LVDS differential pair. Where num represents the pin number.
Generally, when drawing the FPGA schematic, the pins of the same function and purpose are placed in a block diagram, as shown in Figure 2.3, which is a schematic diagram of the user I/O.
(2) Configure the pin.
MSEL[1..0]: Used to select the configuration mode. FPGAs have a variety of configuration modes, such as active, passive, fast, normal, serial, parallel, etc., which can be selected by this pin.
DATA0: FPGA serial data input, connected to the serial data output pin of the configuration device.
DCLK: The FPGA serial clock output that provides the serial clock for the configuration device.
nCSO (I/O): FPGA chip select signal output, connected to the nCS pin of the configuration device.
ASDO (I/O): FPGA serial data output that is connected to the ASDI pin of the configuration device.
nCEO: Download chain device enable output. In a download chain (Chain), when the first device configuration is complete, this signal will enable the next device to begin configuration. The nCEO of the last device in the download chain should be left floating.
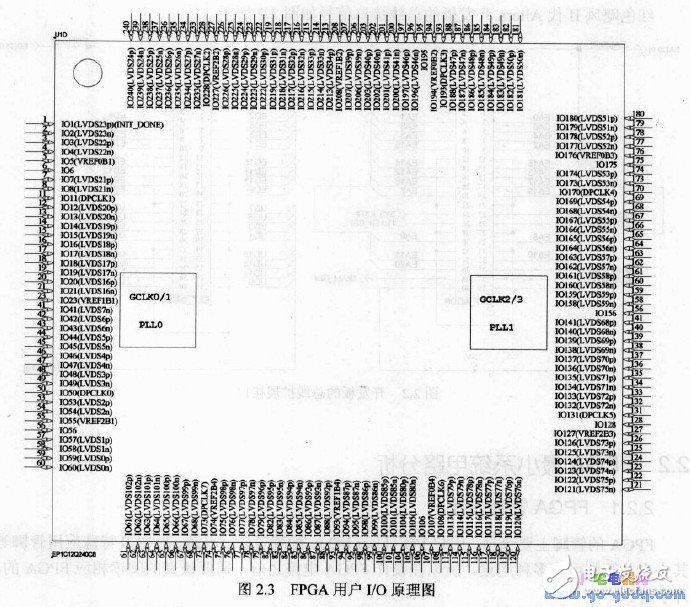
Figure 2.3 FPGA User I/O Schematic
nCE: Downloads the chain device enable input to connect to the nCEO of the previous device. The nCE of the first device in the download chain is grounded.
nCONFIG: User mode configuration start signal.
nSTATUS: Configuration status signal.
CONF_DONE: Configuration end signal.
Figure 2.4 shows the schematic diagram of the FPGA configuration pin.

Figure 2.4 FPGA Configuration Pin Schematic
(3) Power pin.
VCCINT: Core voltage. It is usually related to the process used in the FPGA chip, such as 1.5V for the 130nm process and 1.2V for the 90nm process.
VCCIO: Port voltage. Generally 3.3V, it can also support a variety of voltages, such as 5V, 1.8V, 1.5V and so on.
VREF: Reference voltage.
GND: Signal ground.
(4) Clock pin.
VCC_PLL: Phase-locked loop pin voltage, directly connected to VCCIO.
VCCA_PLL: Phase-locked loop analog voltage, typically connected to VCCINT through a filter.
GNDA_PLL: Phase-locked loop analog ground.
GNDD_PLL: Phase-locked loop digital ground.
CLKnum (LVDSCLKnump): Phase-locked loop clock input. Support LVDS clock input, p is connected to the positive terminal, and num is the PLL serial number.
CLKnum (LVDSCLKnumn): Phase-locked loop clock input. Support LVDS clock input, n is connected to the negative terminal, and num indicates the PLL serial number.
PLLnum_OUTp (I/O): Phase-locked loop clock output. Support LVDS clock input, p is connected to the positive terminal, and num is the PLL serial number.
PLLnum_OUTn (I/O): Phase-locked loop clock output. Support LVDS clock input, n is connected to the negative terminal, and num indicates the PLL serial number.
Figure 2.6 shows the schematic diagram of the FPGA clock pin.

Figure 2.5 Schematic diagram of FPGA power supply pin Figure 2.6 FPGA clock pin schematic
In addition, some of the FPGA pins are global clocks, which have been clocked in the FPGA. Use these pins as critical clock or signal routing for optimum performance.
(5) Special pins.
VCCPD: Used to select the drive voltage.
VCCSEL: Used to control the input buffer voltage associated with the configuration pins and phase-locked loops.
PORSEL: Power-on reset option.
NIOPULLUP: Used to control whether the internal pull-up resistor of the user I/O used in the configuration works.
TEMPDIODEn/p: Used to correlate temperature sensitive diodes.
1500 Puffs Vape,E-Cigarette 1500 Puffs,Disposable Vape Pen E-Cigarette,All-In-One Electronic Cigarette
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigaretteyfactory.com