The so-called virtual reality is to deceive people's eyes and brain, so that the virtual world feels like the real world. At present, good VR products have done quite well in this respect, but there is still room for improvement. The next thing to say is a technology that allows the virtual world to better simulate the real world.
Human eyes see the world and VR rendering
The range that the human eye can see is limited, thus creating a noun called human vision. Human eyesight refers to the angle of view when a person does not move his head. We are in a 360-degree world, but at any time we can only see things in the 120 degree range, and our eyes will focus on a small area of ​​no more than 6 degrees in the field of view (central + near central) The concave field of view is surrounded by blurry (peripheral vision), which is how we see the world.
The top-of-the-line VR headlights (HTC Vive, Oculus Rift) have a viewing angle of around 110 degrees (depending on the distance between the eye and the screen), which is very close to the human eye. The world we see in the VR headline is only part of what it displays on the screen, and the real focus is on a small area of ​​this small part. However, when the VR device renders the image, it renders the entire field of view, and does not refresh at the same speed as the image that is focused by the human eye.
Due to the high resolution and refresh rate of VR devices, this rendering method requires a lot of GPU resources, making the helmet of the PC platform very demanding on the graphics card (usually above GTX 970), while mobile VR is difficult to achieve a good experience. .
However, some companies are already working on solving problems. Nvidia has introduced MRS (mulTI-resoluTIon shading) technology, and domestic company Qixin Yiwei hopes to add Foveated rendering technology.
Partition rendered MRS
Last May, Nvidia added MRS technology to its own VR developer suite, GameWorks VR. This technique makes rendering for VR no longer to render the entire image at the same resolution, but is divided into several different areas.
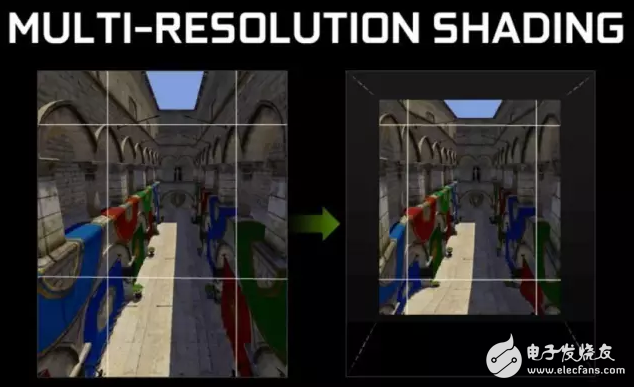
The center of the picture, which is the main area that the human eye sees in the VR, is also where the picture is not distorted, and is rendered with full high resolution; while the edges of the picture are rendered with lower quality, plus edges The pixel's loss after deformation can save 25%-50% of the pixels, theoretically can double the rendering effect.
Graphics cards using the Nvidia Maxwell architecture, including the GeForce TItan X and GTX 900 series, currently support this technology.
In an interview with Lei Feng.com, Nvidia's global vice president and general manager of China, Zhang Jianzhong also explained the technology:
The traditional glasses are fisheye. The traditional GPU renders a rectangle, and the rectangle becomes a fisheye. It is impossible to use traditional methods to render. So we thought of a clever way. We divided the visual graphics into nine pieces and rendered them in different ways, which increased the efficiency by about 50%. The result is equivalent to a 90-frame rendering in the past, and now you can do about 140 frames, so you can see higher definition.
Focus rendering
Domestic startup Qixinyi is currently working with Nvidia to further develop focus rendering technology (also known as gaze point rendering) using eye tracking technology based on MRS technology to further reduce the area of ​​HD rendering.
According to Huang Xinbing, CEO of Qixin Yiwei, the focus rendering uses the near-infrared sensor to track the eyeball of the person, and judges the gaze point of the human eye. Only the gaze point area is rendered in high definition, and this area changes with the change of the gaze point. .
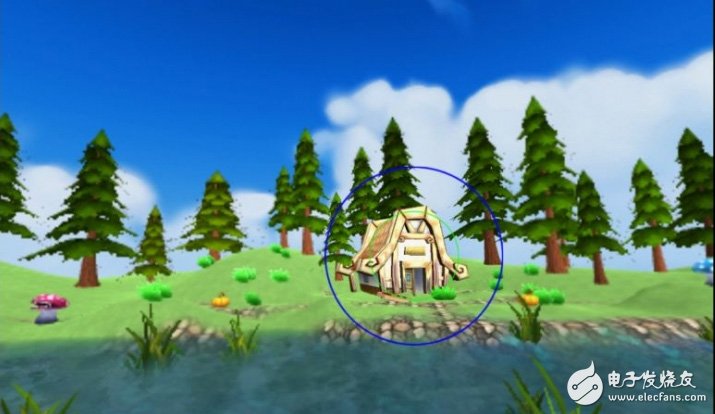

The picture above shows the screen displayed by Lei Feng.com on the computer screen when trying to use the gaze point rendering technology. When the reporter's line of sight stays on the hut, only the hut in the picture is clear, and a large area around it is blurred. But when you look at the helmet, you can hardly tell the difference between a picture that doesn't use this technology.
The official said that this solution can reduce the rendering pixels to about 10% of the MRS solution while ensuring the user experience. The proportion of PCs that can be adapted to VR devices can be increased to 30%.
Eye tracking will bring delay to the whole picture rendering. Huang Tongbing said that they solved this problem. He said that the current tracking technology can achieve a refresh rate of 380Hz. If it is calculated by the usual 220Hz, it will bring a delay of 5ms to the rendering. . However, due to the use of focus rendering, the burden on the GPU is reduced, so that the rendering delay can be reduced to 5ms, and finally the overall delay is still less than 20ms.
There are still some problems to be solved in this technology, including for glasses users, glasses will affect the eye tracking effect; and Fresnel lenses used in products such as HTC Vive, the concentric circles will also interfere with the signal.
There are also vendors in the world that are developing similar technologies, including Tobii, SMI, FOVE and Eyefluence, but there is no standard in this area.
In addition to cooperation with Nvidia, Qixin Yiwei is also working with Qualcomm, HTC, Oculus and domestic VR head-end manufacturers to research this technology. The specific product launch time remains to be determined, but it is reported that Qualcomm's all-in-one solution will focus on This technology, domestic big friends and 3Glasses are also very active
Shenzhen Xcool Vapor Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.xcoolvapor.com