If you want to say that the current advanced technology on the mass production engine, Volkswagen's TFSI will have a place. In 2004, the first TFSI engine was introduced, and the EA888 series released by Volkswagen in 2006 was put into production in China in March 2007. As of July last year, a total of 1 million units were produced. The basic Volkswagen B-Class, Audi A4L And the Q5 and most of the Skoda's 2.0T models are equipped with this engine, definitely called the Volkswagen "star" engine.
This article refers to the address: http://
Now Volkswagen wants to introduce the third generation of this engine in China. Compared to the second generation, the third generation EA888 has many technologies that were first applied to mass production engines. Can these dazzling technologies really add points to the third-generation EA888? Can this third-generation EA888 with technical highlights replace the previous generation as the “Star of the Day� Or look at the third generation. How is your family?
Typical German engineer's idea: the exhaust manifold built into the cylinder head
Among the highlights of the third-generation EA888 technology listed by Volkswagen, the most striking is the exhaust manifold built into the cylinder head. While other technologies have also appeared on mass production engines for the first time, the technology is relatively unique.
Those who are familiar with the engine structure know that the shape of the cylinder head structure of the engine is very complicated, and it is necessary to install the exhaust camshaft, the intake and exhaust valves, the valve rocker arm, the spark plug, the intake and exhaust passage, the cooling water channel, etc. With injectors, Volkswagen now wants to add an exhaust manifold to a small space. In addition to increasing complexity, the height of the cylinder head must increase and the engine height will increase.
In addition, the temperature of the engine exhaust manifold is very high, and the exhaust end temperature of the four-cylinder engine is mostly between 900K-1100K (about 626-826 °C), while the exhaust manifold and the cylinder head have different heat dissipation requirements. Therefore, it is also necessary to solve the cooling problem and redesign the cooling pipe. It can be said that such changes require a lot of manpower and material resources in design and verification. So, what is the purpose of the public to change this?
In the view of car cloud, Volkswagen's goal is to reduce the intake air temperature and pressure of the turbocharger, thereby reducing the turbine load and increasing the turbine life. At the same time, because cooling before entering the turbine is equivalent to increasing the intake air temperature limit of the turbine, it allows the engine to have a higher exhaust temperature, which means that the engine's output power and torque can be adjusted higher. In this way, the presence of the intercooler is also made available, and the structure of the turbine can be simplified.
As shown in Figure 1, the difference in output torque between the third-generation 1.8-liter EA888 and the second-generation 1.8-liter EA888 is quite obvious. The power performance of the third-generation 1.8-liter EA888 is closely related to the second-generation 2.0-liter version. Among them is the credit of the built-in exhaust manifold of the cylinder head.
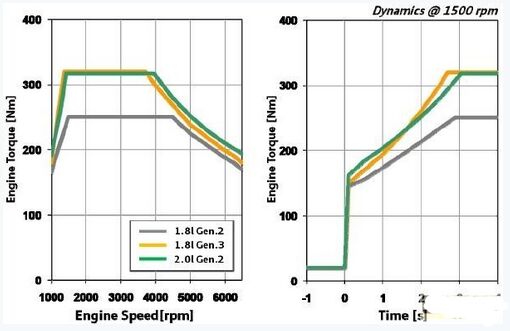
Figure 1 Comparison of the performance curves of the third generation 1.8-liter EA888 and the second-generation two versions

Figure 2 exhaust manifold structure
The final structure of the third generation EA888 exhaust manifold is shown in Figure 2, adjacent to the cooling water channel in the cylinder head. Under such a structural arrangement, heat exchange in the cylinder head takes place in a small space, and the temperature of the exhaust manifold is high, so there is an extreme temperature gradient. In order to optimize the thermal and thermo-mechanical performance of the engine, taking into account the cooling effect under different loads, it is also necessary to consider the castability and feasibility of mass production. It is a very difficult challenge for the public, and it is also a difficult and difficult way to please. .
Finally, through the design of the cross section of the cylinder head gasket, the flow of cooling water on the cylinder head and the cylinder block is adjusted and divided: 75% of the cooling water circulates in the cylinder head, and the cooling of the exhaust manifold is carried out; the remaining 25 % circulates between the cylinder block and the cylinder head to cool the cylinder block and the cylinder head. This part of the cooling pipe also passes through the exhaust manifold to enhance the cooling effect. In the cooling of the exhaust manifold, the cooling of the entire area of ​​the thermal stress concentration is particularly important, otherwise the temperature is too high, and local cooling water boiling is likely to occur.
At the beginning of the development, due to the complex heating conditions in the cylinder head, the conventional simulation algorithm could not meet the requirements. Volkswagen also developed some new algorithms for this purpose. Volkswagen said in the promotion of this engine that this is the world's first exhaust manifold designed using this method. Of course, the average car manufacturer will not use such a complicated algorithm, because no one would have thought of using the cooling water channel in the cylinder head to cool the exhaust.
Perhaps the benefit of such a turbocharger is obvious, that is, the life is improved and the mechanism is streamlined, but at the cost of the complexity of the cylinder head structure and the increase in load, the life expectancy will certainly be affected. In addition, from Figure 3, compared with the previous generation of the engine as a whole, the boiling strength of the starting moment is greatly increased. From the maintenance point of view, it is difficult to say that it is really optimized. The typical German engineer's thinking: to create a brand new thing to solve The inherent problems then create new ones.
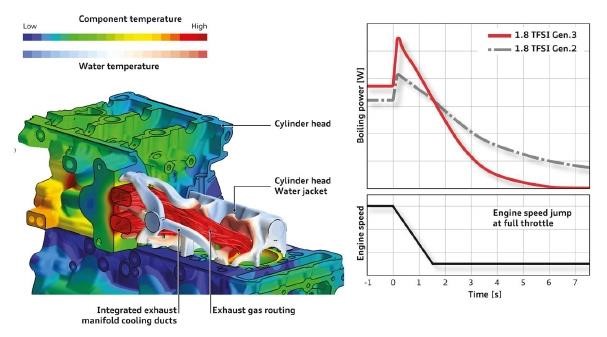
Figure 3 Cylinder head heating simulation algorithm
In the name of fineness: friction optimization design and thermal management system
Although the design of the built-in exhaust manifold of the cylinder head can not help but want to spit, the flash point of the third-generation EA888 technology will not be covered by this, such as the refined friction and thermal management system.
In the third generation of EA888, all major friction-related components were redesigned. For example, piston bushings and piston rings are modified to reduce friction with the cylinder; the size of the crankshaft bearings is moderately reduced to reduce design margins, avoid unnecessary waste and unify life; The switching piston cooling nozzle enhances the cooling process and the cooling effect under low load, further improving the crankshaft transmission performance; and the variable pressure/flow oil pump reduces the engine's thermal load.
In order to reduce fuel consumption, Volkswagen has also put a lot of effort into the thermal management system. In addition to using the electronically controlled coolant thermostat for the first time, the cooling cycle is also set to be finer.
The electronically controlled coolant thermostat can be set to allow the coolant to remain stationary during engine start-up for faster warm-up. When it is detected that the temperature of a certain component of the system reaches the set temperature, the rotary valve will open a certain angle according to the need, so that the coolant will flow out slowly at the minimum flow rate, and will not affect the warming machine.
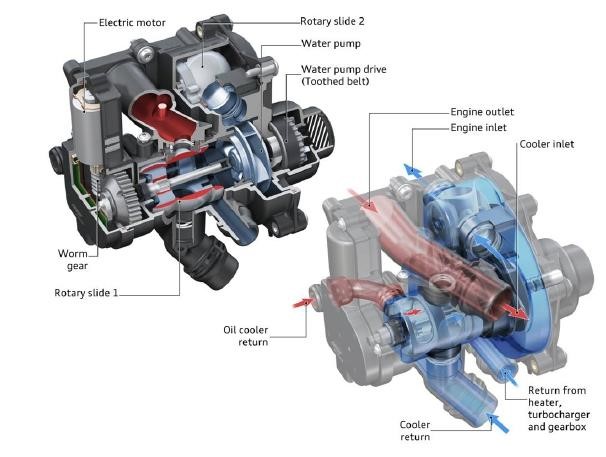
Figure 4 Electronically controlled coolant thermostat
As the engine operating temperature increases, the oil/water heat exchanger (controlled by the electronically controlled coolant thermostat) and the heat exchanger of the transmission (controlled by the additional switchable switch), which are also used for temperature control, start in sequence. jobs. When the temperature of the coolant reaches 107 ° C, the coolant thermostat is introduced into the cooling water in the engine main cooler to ensure that the temperature of the coolant does not exceed the set value. The electronically controlled coolant thermostat can set the maximum temperature of the coolant according to different working conditions of the engine to improve the thermal efficiency of the engine under all working conditions.
The busbar protection box is made of radiation crosslinked polyolefin material with excellent physical, chemical and electrical properties.
It is the insulation treatment material where the busbar is connected.
It is also suitable for 1KV/10KV/35KV voltage grade, with "I", "T", "L" and other shapes of protection boxes. It is widely used in electronics, communication, machinery, manufacturing and other fields.
The specific gravity is small (only 0.9-0.95) and the window rate is high.
It seems that the purchase price is high and the actual use cost is low.
It can provide insulation and enhancement
for busbar connectors.And supply protection and insulation in switches and
substations.
Features:
1.Suitable for 1-35KV.
2.Radiation cross linking materials
(Polyolefin or EPDM rubber ).
3.Quick and easy installation.
4.Avoid short circuit and leakage.
5.Facilitate routine inspection and
maintenance.
6.Resistant to moisture and dust.
7.Meet RoHS Stand.
8.Customized.
Bushing Cover For Busbar,High Voltage Busbar Connector,Busbar Insulator Material,Substation Switch Bushing Insulation Cover
CAS Applied Chemistry Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.casac1997.com