The difference between plasma and serum
1. Ingredients
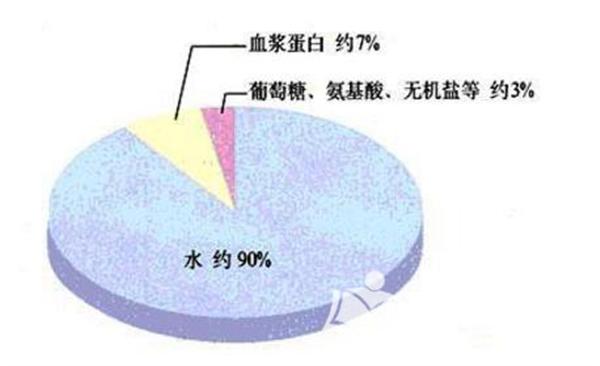
Plasma: Normal people take blood from the blood vessels and add anticoagulant. After centrifugation, the lower part is blood cells. The pale yellow part is called plasma, and there are 5th and 8th coagulation factors and fibrinogen. Among the chemical components of plasma, water accounts for 90-92%, and the other 10% is mainly composed of solute plasma proteins, and contains electrolytes, nutrients, enzymes, hormones, cholesterol and other important components. Plasma protein is a general term for a variety of proteins, which can be divided into three categories: albumin, globulin and fibrinogen by salting out.
Serum: normal human blood extracted from blood vessels without anticoagulant, naturally coagulated, precipitated by centrifugation, the red part below is the blood cell part, the pale yellow part is called serum, there is no 5th, 8th coagulation factor and fibrinogen .
2, the role
The main role of plasma is to supply blood cells, transport the substances needed to maintain human life and the waste generated in the body. Plasma is equivalent to the interstitial material of connective tissue. Plasma is an important part of the blood. Because fibrinogen can be converted to fibrin and has a coagulation effect, plasma is generally used in patients with extensive burns.
The role of serum is to provide essential nutrients, to provide hormones and various growth factors, to provide binding proteins, to provide pro-contact and extension factors to protect cells from mechanical damage, and to provide some protection to cells in culture. Serum can also be used to test blood types.
3, blood coagulation reaction
In the coagulation reaction, platelets release many substances, and each clotting factor also changes. These components are left in the serum and continue to change, such as prothrombin to thrombin, and gradually disappear or disappear with the serum storage time. These are also differences from plasma. However, a large number of substances that did not participate in the blood coagulation reaction were basically the same as plasma. In order to avoid the interference of anticoagulants, the analysis of many chemical components in the blood uses serum as a sample.
Plasma and serum identification methods
Serum identification method
A pale yellow transparent liquid that is coagulated by blood. If the blood is taken out from the blood vessel and placed in a test tube without an anticoagulant, the blood coagulation reaction is activated, and the blood rapidly solidifies to form a jelly. The clot is contracted, and the pale yellow transparent liquid deposited around it is serum, which can also be obtained by centrifugation after coagulation. During the blood coagulation process, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin blocks, so there is no fibrinogen in the serum, which is the biggest difference from plasma. In the blood coagulation reaction, many substances are released from platelets, and each clotting factor also changes. These components are left in the serum and continue to change, such as prothrombin to thrombin, and gradually disappear or disappear with the serum storage time. These are also differences from plasma. However, a large number of substances that did not participate in the blood coagulation reaction were basically the same as plasma. In order to avoid the interference of anticoagulants, the analysis of many chemical components in the blood uses serum as a sample.
Plasma identification method
Plasma is a liquid component of blood in which blood cells hang. The human body contains 2750-3300 ml of plasma, which accounts for about 55% of the total blood volume. The vast majority of plasma is water (90% by volume), in which the dissolved substances are mainly plasma proteins, including glucose, inorganic salt ions, hormones, and carbon dioxide. The main function of plasma is to carry blood cells, and it is also the main medium for transporting secreted products.
The fresh blood is centrifuged to sediment the blood cells, and the upper layer of pale yellow serum is plasma. The difference between plasma and serum is that serum does not contain blood clotting factors such as fibrinogen.
Serum main component
Serum is a very complex mixture of plasma-depleted fibrinogen. Although most of its components are known, some of them are still unclear, and serum composition and content often follow the sex, age, and physiology of blood-feeding animals. Conditions and nutritional conditions vary. Serum is a gelatinous liquid containing no fibrinogen in plasma, and has the functions of maintaining normal viscosity, pH, and osmotic pressure of blood. It is mainly composed of water and various chemical components including albumin, α1, α2, β, γ-globulin, triglyceride, total cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase and the like. The serum contains various plasma proteins, peptides, fats, carbohydrates, growth factors, hormones, inorganic substances, etc., which are physiologically balanced for promoting cell growth or inhibiting growth activity. Although there has been great progress in the study of the composition and action of serum, there are still some problems. mainly:
First: there may be hundreds of serum components. The exact composition, content and mechanism of action are still unclear, especially for some of the peptide growth factors, hormones and lipids. Research work brings many difficulties;
Second: the serum is produced in batches, the difference between the batches is very large, and the serum preservation period is up to one year. Therefore, it is extremely difficult to ensure the similarity of each batch of serum, so that the standardization and continuity of the experiment are limited;
Third: It cannot be ruled out that serum contains volatile substances, which is considered to be one of the causes of "deterioration in the bottle".
Serum preservation precautions
(1) Serum that requires long-term storage must be stored in a -20 ° C - 70 ° C low temperature refrigerator. Do not store in the refrigerator at 4 °C for more than 1 month. Since the volume of the serum will increase by about 10% when frozen, the serum must be reserved for a certain volume before it is frozen into the low-temperature refrigerator, otherwise it may be contaminated or the glass bottle may be cracked.
(2) Heat inactivation refers to the defrosting of the fully thawed serum at 56 ° C for 30 minutes. Shake it regularly during heating. The purpose of this heat treatment is to inactivate the complement in the serum. This heat treatment is generally not recommended unless necessary, as heat treatment can cause a significant increase in serum deposits and can also affect serum quality. Complement participation reactions include: cytotoxicity, contraction of smooth muscle cells, histamine release from mast cells and platelets, enhanced phagocytosis, and chemical chemotaxis and activation of lymphocytes and macrophages.
(3) The thawing of bottled serum requires a gradual thawing method: -20 ° C to -70 ° C The serum in the low temperature refrigerator is dissolved in a refrigerator at 4 ° C for 1 day. Then, it was transferred to room temperature, and then completely dissolved before being dispensed. During the dissolution process, it should be gently shaken evenly (be careful not to cause bubbles) to make the temperature and composition uniform, reducing the occurrence of precipitation. Do not directly thaw the serum from -20 ° C into 37 ° C, so that because the temperature changes too much, it is easy to cause protein aggregation and precipitation.
(4) The serum supplied by the general manufacturer is sterile and does not need to be filtered and sterilized. If serum is found to be suspended, the serum can be added to the culture medium for filtration. Do not directly filter the serum.
(5) Precipitate floc in serum: mainly caused by denaturation of lipoprotein in serum and fibrin in serum after thawing, these flocs do not affect the quality of serum itself. It can be removed by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes or without treatment. "Little black spots" under the microscope: After heat-treated serum, the formation of precipitates is significantly increased. Some sediments are observed under a microscope like "small black spots" and often mistaken for serum contamination. In general, this small black spot does not affect cell growth, but if serum quality is suspected, stop using it immediately and replace another batch of serum.
(6) Do not leave the serum at 37 °C for too long, otherwise the serum will become cloudy, and the active ingredients in the serum will be destroyed and affect the serum quality.
Incremental Encoder is commonly used, and Absolute Encoder is used if there are strict requirements on position and zero position. Servo system should be analyzed in detail, depending on the application situation. Commonly used incremental encoder for speed measurement, which can be used for infinite accumulation measurement; Absolute encoder is used for position measurement, and the position is unique (single or multiple turns). Finally, it depends on the application situation and the purpose and requirements to be realized.
Incremental Linear Encoders,Linear Optical Encoder,Linear Position Encoder,Encoder Bearing Tester
Yuheng Optics Co., Ltd.(Changchun) , https://www.yhenoptics.com