Axiom Precision Medicine Research Chip
time:
2017-09-13
source:
unknown

Compared with traditional empirical medicine and evidence-based medicine, precision medicine is a new concept, method and practice of medical development. It pays more attention to comprehensive consideration of each individual's genetic, environmental and lifestyle aspects in the diagnosis and treatment process. Differences to achieve accurate prevention, diagnosis and disease management for individuals. Precision medicine has become a hot spot in the field of molecular biology research. In the current relatively high cost of whole genome sequencing, in order to meet the huge market demand for precision medicine, Affymetrix launched this ultra-cost-effective AxiomTM precision medical research chip (PMRA) designed for precision medicine in 2016. , Precision Medicine Research Array). The chip contains 900,000 SNP probes, and the SNP markers cover the entire genome on average, meeting the needs of genome-wide association analysis and genetic linkage analysis. In addition, PMRA also includes the SNP site in the latest GWAScatalog database (updated to May 2016), reflecting almost the latest clinical research results. Designed for scientists in basic laboratory and clinical laboratories, research institutions, and direct-to-consumer genomic analysis organizations, PMRA helps scientists better understand the interaction between human genetics and susceptibility to complex diseases. Serve as a task for susceptibility locus detection and genotyping, providing guidance on medications and treatment options
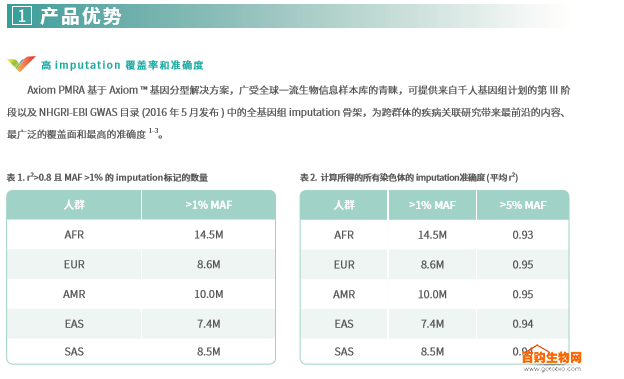
The Axiom PMRA GWAS marker is a common variant screened using a patent-based marker selection strategy based on imputation, covering the entire genome of five major groups. These groups include the African (AFR), European (EUR), Mixed American (AMR), East Asian (EAS) and South Asian (SAS) populations defined by the Thousand Genome Project. Table 1 lists the number of imputation markers for the five ancestral populations on the Axiom PMRA; Table 2 lists the imputation accuracy for the GWAS markers with a minimum allele frequency (MAF) >1% and >5%.
Covering clinical to disease variation
Contains carefully selected, clinically significant pathogenic mutations, including those that are associated with actual genetic risk in a broad population.Covering common cancer-related mutations
Covers common cancer-related variability identified by GWAS as required by NHGRI-EB.
Coverage immunization, transplant-related variation
Includes human leukocyte antigen (HLA) markers that can be analyzed using the corresponding AxiomTM HLA analysis software, as well as killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs), designed to deepen understanding of the risks and causes of rejection in transplant-related studies4.Covering blood phenotype markers
Covers blood phenotypic markers selected from GWAS and candidate gene studies, including markers associated with the regulation of red blood cell populations, red blood cells and platelets, and blood balance regulation.Easy sample tracking
SNPs provided by the University of Washington and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology-Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard were used as fingerprint SNPs. These markers are shared across multiple mainstream genotyping platforms for sample tracking.high performance
Axiom PMRA meets the needs of many years of precision medical cohort research, providing high-density genotyping chips with reproducible results and no loss of SNP markers between batches. Genotyping performance evaluations were performed on 288 samples, including samples from the international HapMap project, using stringent quality control criteria including average sample identification, sample consistency, and reproducibility (Table 3).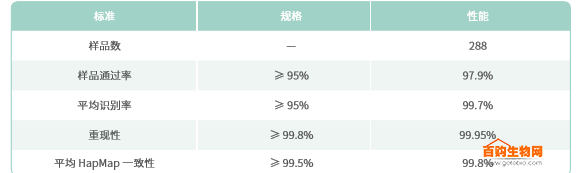
Guarantee research continuity
Accurate medical programs involving large-scale cohort studies typically last for years, exploring clinical markers, pharmacogenomic markers, and immune-related markers for a variety of diseases to gain insight into important diseases and conditions. This type of long-term research requires 100% specific chip content and a technology platform that guarantees years of supply. There are batch-to-batch variations in bead-based technology, and there may be a loss of SNP per manufacturing lot, unlike the Axiom chip process, which uses manufacturing techniques to ensure 100% fidelity and is guaranteed as needed by the customer. Each manufacturing lot contains all the tags.
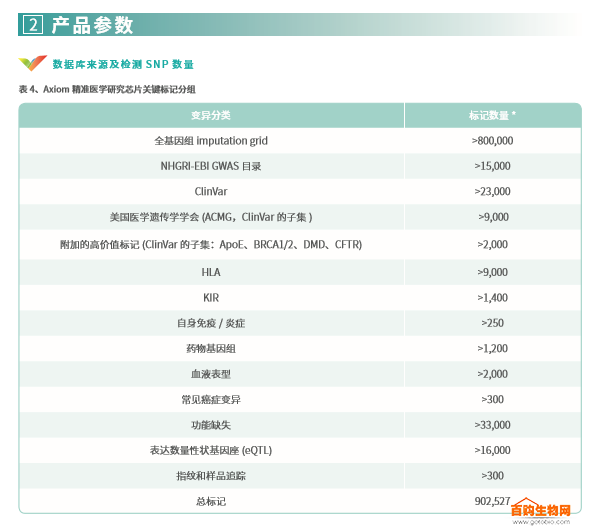
Covering variations in disease and human health
Axiom PMRA contains thousands of new risk variants involving human diseases and health conditions. The chip contains a causal variant selected from ClinVar, including the ApoE marker associated with Alzheimer's disease 5,6 . So far, there are no other chip products that offer such tags. Table 5 lists the number of multiple tags sorted by OMIM and ClinVar databases.
Cancer risk variation
The chip covers more than 17,000 cancer risk variants from the NHGRI-EBI GWAS catalog, multiple publications, and the OMIM database. These include variations associated with rectal cancer 7, prostate cancer 8, ovarian cancer 9, lung cancer 10, and breast cancer.Mental health, behavioral, and neurodevelopmental related variables
This category covers more than 19,000 variants, one of which is based on the results of the UK Biobank AxiomTM chip, which is associated with neurosis,11,12.Immune-related mutations (including autoimmune and inflammatory variants)
The chip covers more than 200 sites contained in the UK Biobank Axiom chip, and the BioNet provides evidence of certain specific autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Type I diabetes, http:// diffuse toxic goiter, Hashimoto's thyroiditis and celiac disease. The chip also includes novel variants involving narcolepsy 13 and has been evaluated in transplantation studies4.Loss of function (LoF) variation
The tag contained in the chip detects genetic alterations that are expected to completely disrupt the function of the protein-coding gene, including the rare and potentially toxic LoF allele, mutations expected to cause severe disease, and common LoF mutations in non-critical genes. The chip contains more than 1,000 autosomal recessive variants and more than 500 autosomal dominant predictive variants.Cardiovascular disease variation
These variations cover the most common cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease, familial hypercholesterolemia, familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Marfan syndrome, and congenital long QT syndrome.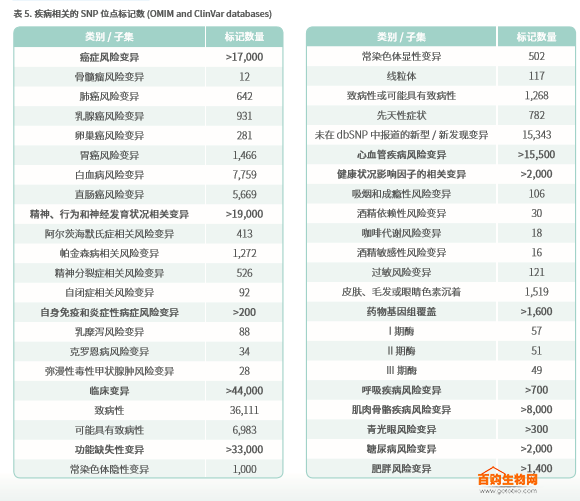

1. Ma J., et al. Association analysis of the cubilin (CUBN) and megalin (LRP2) genes with ESRD in African Americans. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 11(6): 1034-1043 (2016).
2. Davies G., et al. Genome-wide association study of cognitive functions and educational attainment in UK Biobank (N=112 151). Molecular Psychiatry 21:758–767 (2016).
3. Day FR, et al. Physical and neurobehavioral determinants of reproductive onset and success. Nature Genetics 48:617–623 (2016).
4. Li YR, et al. Concept and design of a genome-wide association genotyping array tailored for transplantation-specific studies. Genome Medicine 7:90 (2015).
5. Lambert JC, et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identification 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer's disease. Nature Genetics 45(12): 1452–1458 (2013).
6 Joshi PK, et al. Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan. Nature Communications 7:11174 (2016).
7. Al-Tassan NA, et al. A new GWAS and meta-analysis with 1000 Genomes imputation labeled novel risk variants for colorectal cancer. Scientific Reports 5:10442 (2015).
8. Hoffmann TJ, et al. Imputation of the rare HOXB13 G84E mutation and cancer risk in a large population-based cohort. PLoS Genetics 11(1):e1004930 (2015).
9. Permuth JB, et al. Exome genotyping arrays to identify rare and low frequency variants associated with epithelial ovarian cancer risk. Human Molecular Genetics doi:10.1093/hmg/ddw196 (2016).
10. Kachuri L., et al. Fine mapping of chromosome 5p15.33 based on a targeted deep sequencing and high density genotyping identified novel lung cancer susceptibility loci. Carcinogenesis 37(1): 96–105 (2016).
11. Gale CR, et al. Pleiotropy between neuroticism and physical and mental health: findings from 108,038 men and women in UK Biobank. Translational Psychiatry 6:e791 (2016).
12. Smith DJ, et al. Genome-wide analysis of over 106,000 individuals identifies 9 neuroticism-associated loci. Molecular Psychiatry 21(6): 749–757 (2016).
13. Han F., et al. Genome wide analysis of narcolepsy in China implicates novel immune loci and reveals changes in association prior to versus after the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic. PLoS Genetics 9(10):e1003880 (2013).
Micro Data Cable,Charging Data Cable,Micro Usb Data Cable,Micro Usb Transfer Cable
SUNSHINE ELECTRONICS TECH. CO., LTD. , https://www.benefitucx.com